SLF4J
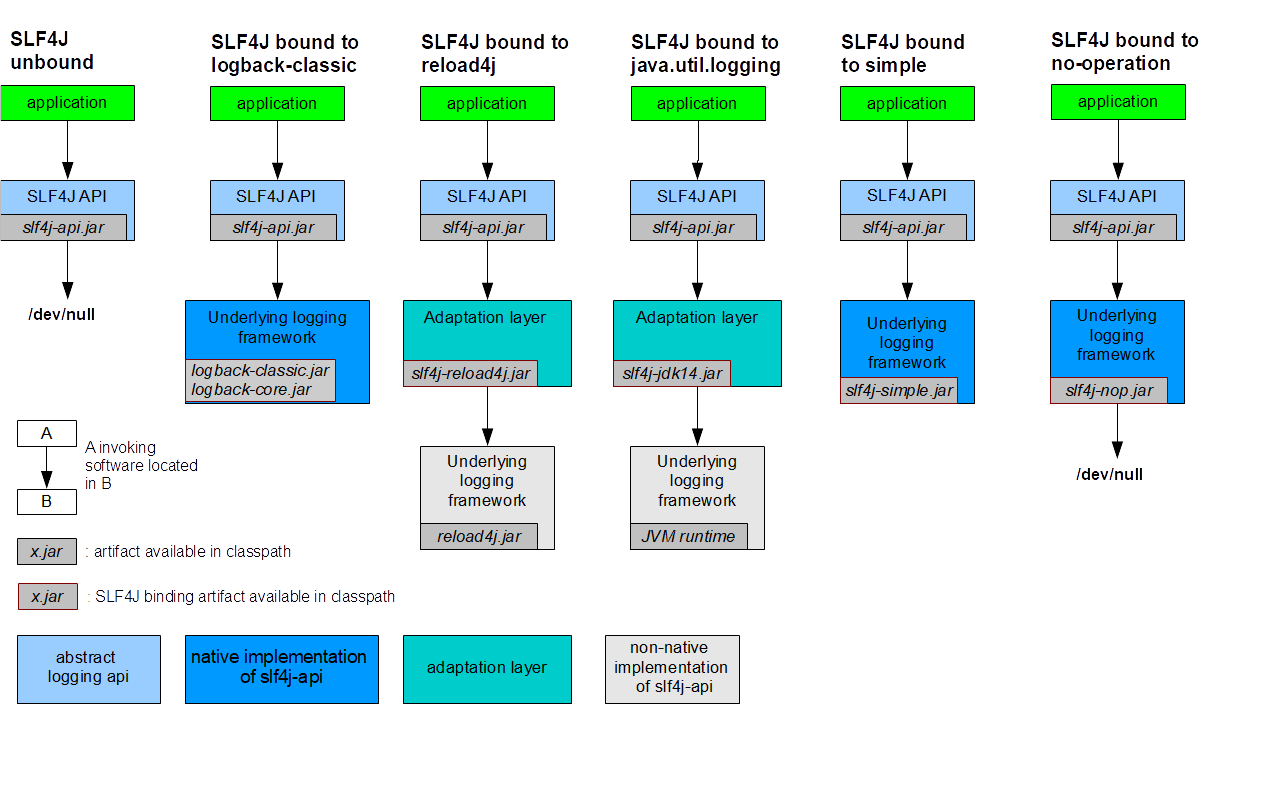
Java 的简单日志外观 (SLF4J - The Simple Logging Facade for Java) 用作各种日志框架(例如 java.util.logging、logback、log4j)的简单外观或抽象,允许最终用户在部署时插入所需的日志框架。请注意,启用 SLF4J 的库/应用程序意味着仅添加一个强制依赖项,即 slf4j-api-1.7.36.jar。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("{} {}", "Hello", "World");
}
}
|
在部署时与日志框架绑定
SLF4J providers (or bindings)
- slf4j-log4j12-2.0.3.jar log4j 1.2 版的绑定/提供程序,一个广泛使用的日志框架。鉴于 log4j 1.x 已在 2015 年和 2022 年宣布 EOL,从 SLF4J 1.7.35 开始,slf4j-log4j模块在构建时自动重定向到 slf4j-reload4j模块。 假设您希望继续使用 log4j 1.x 框架,我们强烈建议您改用 slf4j-reload4j。
- slf4j-reload4j-2.0.3.jar 自 1.7.33 以来 RELOAD4J 框架 的绑定/提供程序 。Reload4j 是 log4j 版本 1.2.7 的直接替代品。您还需要将 reload4j.jar 放在您的类路径上。
- slf4j-jdk14-2.0.3.jar java.util.logging 的绑定/提供程序,也称为 JDK 1.4 日志记录
- slf4j-nop-2.0.3.jar NOP 的绑定/提供者,默默地丢弃所有日志记录。
- slf4j-simple-2.0.3.jar 简单 实现的绑定/提供程序,它将所有事件输出到 System.err。只打印级别 INFO 和更高级别的消息。此绑定在小型应用程序的上下文中可能很有用。
- slf4j-jcl-2.0.3.jar Jakarta Commons Logging的绑定/提供者。此绑定会将所有 SLF4J 日志记录委托给 JCL。
- logback-classic-1.4.2.jar 用于 Jakarta EE,需要 logback-core-1.4.2.jar 或 logback-classic-1.3.2.jar 用于 Javax EE,需要 logback-core-1.3.2。logback 是 SLF4J 的 NATIVE IMPLEMENTATION,不需要 SLF4J bindings/providers。
从 2.0.0 版本开始,SLF4J 绑定被称为提供者。SLF4J API 版本 2.0.0 依赖 ServiceLoader 机制来查找其日志记录后端。
 SLF4J 提供者
SLF4J 提供者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/ch.qos.logback/logback-classic -->
<!-- LOGBACK-CLASSIC 1.3.X (JAVAX EE) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- LOGBACK-CLASSIC 1.4.X (JAKARTA EE) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.4.4</version>
</dependency>
|
Log4j 2 SLF4J Binding
- log4j-slf4j-impl 应与 SLF4J 1.7.x 版本或更早版本一起使用。
- log4j-slf4j2-impl 应该与 SLF4J 2.0.x 版本或更新版本一起使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3</version>
</dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-slf4j2-impl -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="WARN" monitorInterval="30">
<Properties>
<Property name="LOG_PATTERN">%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1} - %m%n</Property>
</Properties>
<Appenders>
<Console name="console" target="SYSTEM_OUT" follow="true">
<PatternLayout pattern="${LOG_PATTERN}"/>
</Console>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Root level="info">
<AppenderRef ref="console"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>
|
MDC 映射调试上下文
MDC (Mapped Diagnostic Context,映射调试上下文) logback 及log4j2 提供的一种方便在多线程条件下记录日志的功能。MDC 可以看成是一个与当前线程绑定的哈希表,可以往其中添加键值对。MDC 中包含的内容可以被同一线程中执行的代码所访问。
当前线程的子线程会继承其父线程中的 MDC 的内容。当需要记录日志时,只需要从 MDC 中获取所需的信息即可。MDC 的内容则由程序在适当的时候保存进去。对于一个 Web 应用来说,通常是在请求被处理的最开始保存这些数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public class LogInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//如果有上层调用就用上层的ID
String traceId = request.getHeader(Constants.TRACE_ID);
if (traceId == null) {
traceId = TraceIdUtil.getTraceId();
}
MDC.put(Constants.TRACE_ID, traceId);
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
//调用结束后删除
MDC.remove(Constants.TRACE_ID);
}
}
|
1
|
<property name="pattern">[TRACEID:%X{traceId}] %d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level %class{-1}.%M()/%L - %msg%xEx%n</property>
|
MDC 存在的问题,丢失traceId的情况,来一个再解决一个,绝不提前优化。
- 子线程中打印日志丢失 traceId
- HTTP 调用丢失 traceId
子线程在打印日志的过程中traceId将丢失,解决方式为重写线程池。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
public class ThreadMdcUtil {
public static void setTraceIdIfAbsent() {
if (MDC.get(Constants.TRACE_ID) == null) {
MDC.put(Constants.TRACE_ID, TraceIdUtil.getTraceId());
}
}
public static <T> Callable<T> wrap(final Callable<T> callable, final Map<String, String> context) {
return () -> {
if (context == null) {
MDC.clear();
} else {
MDC.setContextMap(context);
}
setTraceIdIfAbsent();
try {
return callable.call();
} finally {
MDC.clear();
}
};
}
public static Runnable wrap(final Runnable runnable, final Map<String, String> context) {
return () -> {
if (context == null) {
MDC.clear();
} else {
MDC.setContextMap(context);
}
setTraceIdIfAbsent();
try {
runnable.run();
} finally {
MDC.clear();
}
};
}
}
public class ThreadPoolExecutorMdcWrapper extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
public ThreadPoolExecutorMdcWrapper(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutorMdcWrapper(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutorMdcWrapper(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutorMdcWrapper(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
super.execute(ThreadMdcUtil.wrap(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()));
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
return super.submit(ThreadMdcUtil.wrap(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()), result);
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return super.submit(ThreadMdcUtil.wrap(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()));
}
@Override
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return super.submit(ThreadMdcUtil.wrap(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()));
}
}
|
在使用HTTP调用第三方服务接口时traceId将丢失,需要对HTTP调用工具进行改造,在发送时在request header中添加traceId,在下层被调用方添加拦截器获取header中的traceId添加到MDC中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class RestTemplateTraceIdInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest httpRequest, byte[] bytes, ClientHttpRequestExecution clientHttpRequestExecution) throws IOException {
String traceId = MDC.get(Constants.TRACE_ID);
if (traceId != null) {
httpRequest.getHeaders().add(Constants.TRACE_ID, traceId);
}
return clientHttpRequestExecution.execute(httpRequest, bytes);
}
}
restTemplate.setInterceptors(Arrays.asList(new RestTemplateTraceIdInterceptor()));
|
Log4J 配置
Log4j.appender.FILE.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%t-%x-%-5p-%-10c:%m%n
PatternLayout
如果您希望基于某种模式生成特定格式的日志信息,可使用 org.apache.Log4j.PatternLayout 格式化您的日志信息。
PatternLayout 继承自抽象类 org.apache.Log4j.Layout,覆盖了其 format() 方法,通过提供的模式,来格式化日志信息。
PatternLayout 是一个简单的 Layout 对象,提供了如下属性,该属性可通过配置文件更改:
| 序号 |
属性 & 描述 |
| 1 |
conversionPattern设置转换模式,默认为 %r [%t] %p %c %x - %m%n。 |
模式转换字符
下面的表格解释了上面模式中用到的字符,以及所有定制模式时能用到的字符:
| 转换字符 |
含义 |
| c |
使用它为输出的日志事件分类,比如对于分类 “a.b.c”,模式 %c{2} 会输出 “b.c” 。 |
| C |
使用它输出发起记录日志请求的类的全名。比如对于类 “org.apache.xyz.SomeClass”,模式 %C{1} 会输出 “SomeClass”。 |
| d |
使用它输出记录日志的日期,比如 %d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} 或 %d{dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss,SSS}。 |
| F |
在记录日志时,使用它输出文件名。 |
| l |
用它输出生成日志的调用者的地域信息。 |
| L |
使用它输出发起日志请求的行号。 |
| m |
使用它输出和日志事件关联的,由应用提供的信息。 |
| M |
使用它输出发起日志请求的方法名。 |
| n |
输出平台相关的换行符。 |
| p |
输出日志事件的优先级。 |
| r |
使用它输出从构建布局到生成日志事件所花费的时间,以毫秒为单位。 |
| t |
输出生成日志事件的线程名。 |
| x |
输出和生成日志事件线程相关的 NDC (嵌套诊断上下文)。 |
| X |
该字符后跟 MDC 键,比如 X{clientIP} 会输出保存在 MDC 中键 clientIP 对应的值。 |
| % |
百分号, %% 会输出一个 %。 |
格式修饰符
缺省情况下,信息保持原样输出。但是借助格式修饰符的帮助,就可调整最小列宽、最大列宽以及对齐。
下面的表格涵盖了各种修饰符:
| 格式修饰符 |
左对齐 |
最小宽度 |
最大宽度 |
注释 |
| %20c |
否 |
20 |
无 |
如果列名少于 20 个字符,左边使用空格补齐。 |
| %-20c |
是 |
20 |
无 |
如果列名少于 20 个字符,右边使用空格补齐。 |
| %.30c |
不适用 |
无 |
30 |
如果列名长于 30 个字符,从开头剪除。 |
| %20.30c |
否 |
20 |
30 |
如果列名少于 20 个字符,左边使用空格补齐,如果列名长于 30 个字符,从开头剪除。 |
| %-20.30c |
是 |
20 |
30 |
如果列名少于 20 个字符,右边使用空格补齐,如果列名长于 30 个字符,从开头剪除。 |
附录